|
Discussion Subconsciously, people use ratios of common word in a consistent way but are completely unaware of it. Simple words, such as "at", "the", "I", "to" and so on. In large texts, the ratios of these word may form a sort of fingerprint for a particular author with the values varying only slightly over time. If two pieces of a similar type are written within a few months, the ratios should be approximately the same. We know that if genuine, the Proof of Evidence was
written between the first hearing date of 10th
October 1994 and Tod Potsgrove's death early in
the week of 31st October 1994, having been
supplied with the transcripts of the covertly
recorded tapes at the beginning of that week. On
the first day of the hearing - 10th October1994 -
the company stated that the interlocutory meeting
was a short meeting One serious problem of this type of analysis on the Proof of evidence is that there is so little to go on - several thousand words - hardly a book. Finding enough repetitions of a word to make the sample viable was the first step. Method The text was loaded into a word processor (Lotus Word Pro 97) and all of the words that the automatic spell checker did not recognise were hidden - that is, the hightlighting for those words was turned off. In turn, each test word was placed in the
search and replace function and a non-existent
word that the spell checker would highlight was
replaced used to replace all occurrences of the
test w
As there are 17 paragraphs in the document, a minimum of 60 occuerences was chosen as a compromise between having enough occurrences in each paragraph and having a reasonable number of words to choose from. Once these words had been chosen, the repacement and highlighting process was repeated, this time counting the number of replacements highlighted in each paragraph by the automatic spell checker. These results were noted and then calculeted as percentages of the wordage for each paragraph. Results
Table 2 shows the results expressed as percentages of each paragraph. The results for of, and and that each have a zero and therefore were not used for ratio calculations. The raios for to:the, I:the and I:to were calculated and are included above. In addition to this, the word count for each
section is included to that it can be
Inferences
Table 3 shows the anomalies for each type of anomaly with outstanding anomalies highlighted. Table 4 shows these anomalies for each paragaraph. We can see from Table 3 that there were no significantly low levels of the word to word ratios. In Table 4, we can see that "I" values vary markedly between paragraph 1 (80 words) and paragraph 14a (194 words).
Paragraphs 1 (80 words), 8 (57 words) and 11 (278 words) have the highes numbers of weighted anomolies with paragraphs 1 and 11 having the best distinctions of highs and lows. Paragraphs 12 (166 words), 13 (258 words), The Changes in values involving "I" may possibly be the most important as people tend to talk in a particular way, constructing sentences around rules that influence the proportion of references to themselves in this way. If a piece was being written by someone else, they would be conscious of the number of times "I" was used and, unless they took the trouble to analyse the paragraphs themselves, would have a higher probability of having a significantly different proportion of "I"s. Paragraphs that are remarkable in terms of levels of "I" are 1 (80 words) and 6 (117 words) - high and low respectively - and in proportion of "I/the" are 11 (278 words), 1 (80 words) and 7 (153 words).
The short length of paragraphs 2, 8, 1 and 14 make the results on those paragraphs less reliable therefore, it can be said that, based upon the limited extent of the available material, paragraphs 7, 9 and 11 appear to originate from a sources different to most of the rest of the document and there is a reasonable probability that paragraphs 1 and 8 also originate from a source different to most of the rest of the material. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 of only ten to fifteen minutes when only
passwords were discussed and it was revealed that
in fact, it was bullying session lasting over an
hour as the 1 hour dictaphone tape had ran out.
The Proof of Evidence changes the company's story
to "Whilst the meeting started at 3 o'clock,
I must have left the building by around 4.15pm or
4.30pm, because I know from my diary I was
elsewhere at 5.30pm" therefore this must
have been written after the 10th October 1994.
Tod Potsgrove was, of course, unable to write any
proof of evidence that would be acceptable in a
court after he had died early in the week of 31st
October 1994.
of only ten to fifteen minutes when only
passwords were discussed and it was revealed that
in fact, it was bullying session lasting over an
hour as the 1 hour dictaphone tape had ran out.
The Proof of Evidence changes the company's story
to "Whilst the meeting started at 3 o'clock,
I must have left the building by around 4.15pm or
4.30pm, because I know from my diary I was
elsewhere at 5.30pm" therefore this must
have been written after the 10th October 1994.
Tod Potsgrove was, of course, unable to write any
proof of evidence that would be acceptable in a
court after he had died early in the week of 31st
October 1994.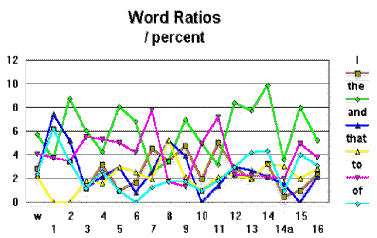 Thus, an
anomaly has to be more significant in the shorter
paragraphs for it to be considered as genuine -
this is the case with paragraph 8 which has a
large proporation of "that"s and a low
proportion of "to"s.
Thus, an
anomaly has to be more significant in the shorter
paragraphs for it to be considered as genuine -
this is the case with paragraph 8 which has a
large proporation of "that"s and a low
proportion of "to"s.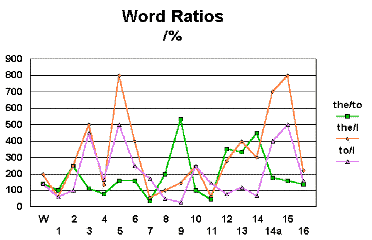 Paragraphs
12, 13 and 16 set the norm for the overall
writing according to this method of analysis and
paragraphs 1, 7, 8, 9 and 11 appearing to be of
different origin. It is,
Paragraphs
12, 13 and 16 set the norm for the overall
writing according to this method of analysis and
paragraphs 1, 7, 8, 9 and 11 appearing to be of
different origin. It is,